
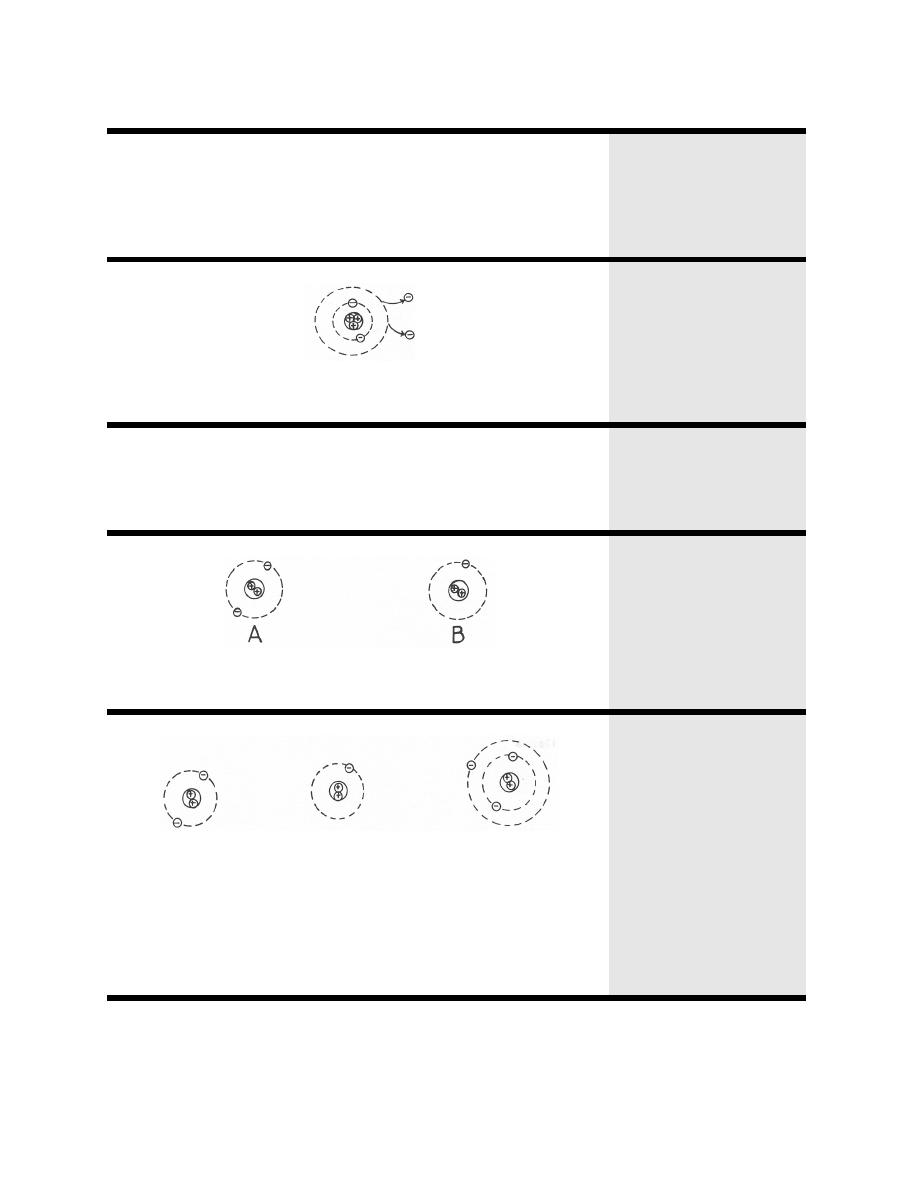
The chemical properties of a substance are determined by the negatively charged electrons enshrouding the nucleus. 01% of the volume of the atom, but typically contains more than 99.9% of the mass of the atom. These are held together by the strongest known fundamental force, called the strong force. Atomic nuclei consist of electrically positive protons and electrically neutral neutrons. The food coloring is carried along in the milk as it retreats from the fats.In 1911, Ernest Rutherford discovered that at the core of every atom is a nucleus. Why does this work? Hint: milk contains fats, and soap repels fats. Mini-Experiment 2: Here's a dramatic experiment you can do with food coloring, dish soap, and milk. Remove the thread and watch what happens. Now add some dish detergent outside the loop of string and gently stir it into the water. Put a few drops of vegetable oil inside the loop of thread and gently stir the oil. Now take a length of thread or a long hair and lay it on top of the water in a closed loop. Mini-Experiment 1: Pour some water into a shallow bowl. When the soapy water is rinsed away, the trapped grease and oil is washed away with it. When a soap micelle encounters oil or grease, these non-polar materials are forced to the inside of the micelle to get away from the polar water and polar heads of the micelle, where they are trapped. When soap is added to water, it forms structures called "micelles." The heads of the soap micelles are polar and the tails, which face inward to retreat from the polar water, are non-polar. So why do soaps and detergents clean our dishes and our clothes? Soaps are chemically similar to cell membranes. With covalent bonds, they have to share them. With ionic bonds, atoms give or take electrons. Here's a little joke to help you remember. Ionic and covalent bonds are the most important in all of chemistry. Atoms that carry a charge, either positive or negative, are called ions and, because opposites attract, they can form an ionic bond. One atom loses electrons (oxidation) while the other one gains electrons (reduction). The formation of an ionic bond is a redox reaction.

When an atom loses an electron, its net charge goes from 0 (neutral) to +1 (positive) The atom that gained an electron (remember that electrons have a negative charge) becomes negatively charged (-1) while the atom that lost an electron becomes positively charged (+1). In other situations, one atom can become more stable by losing electrons and the other can become more stable by gaining them. But they can only share the electron(s) if they stay close to each other, and this is called a covalent bond. One way they can achieve this goal is for two atoms to share one or more electrons between them so that each of them can fill or empty that outermost shell. Atoms become more stable when their outermost electron shells are emptied out or filled up. Atoms of each element have varying numbers of electrons in their outermost shells. The tiny electrons (with negative charges) circle rapidly in orbits around the nucleus, forming electron shells at different distances, much like the planets and other objects that circle the sun. The large protons (with a positive charge) and neutrons (with no charge) are found at the nucleus or center. The structure of an atom is similar to that of the solar system. Chemical Bonds: Atoms seek more stable states.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
